What is portfolio analysis in strategic management?
Portfolio analysis in strategic management involves analyzing every aspect of the product mix to identify and evaluate all products or service groups offered by the company on the market and to prepare detailed strategies for each part of the product mix to improve the growth rate.
It can also be used to make a strategic decision about strategic business units. Portfolio analysis in strategic management has, as its major objective, the optimal gathering of the resources among the business activities comprising a diversified business portfolio.
What is the Portfolio Analysis?
Portfolio analysis is a process of examining all the aspects related to the organization to improve the organization’s profits.
Portfolio analysis aims to identify the components that need to be enhanced to remove barriers to making the working process recognize better methods to allocate resources to improve the return on investment(ROI).
Reasons For Portfolio Analysis
A different purpose for conducting a business portfolio analysis in strategic management. The three main reasons why management focuses on business portfolio analysis in strategic management, are:
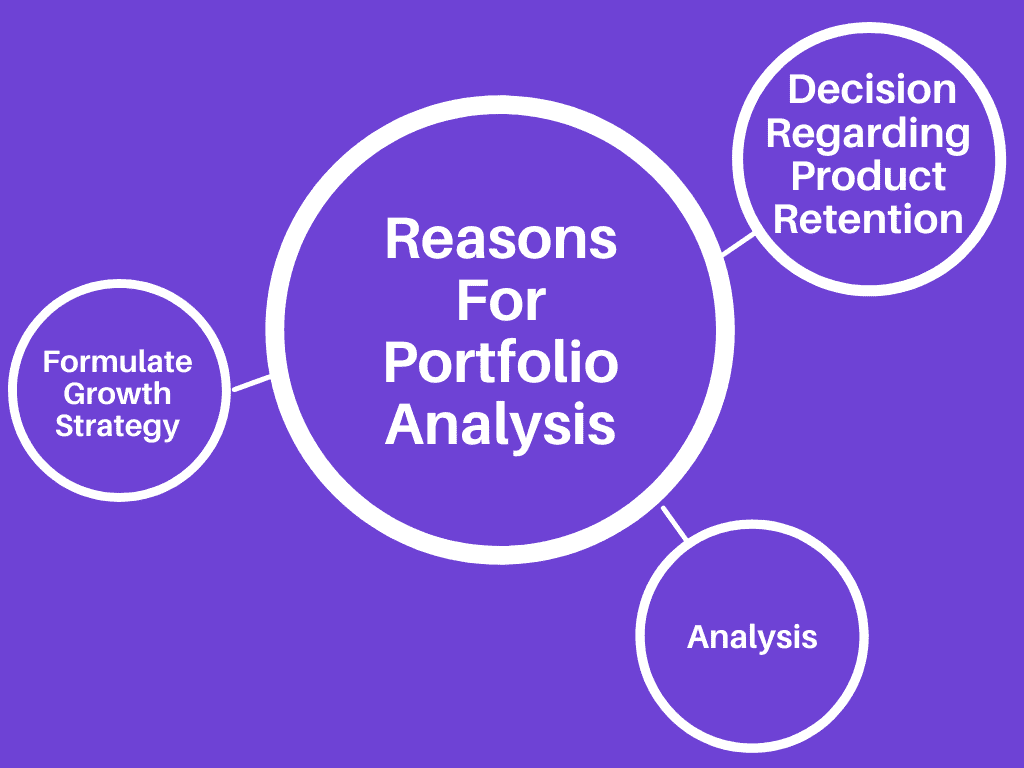
1. Analysis
The organization’s first reason to conduct a portfolio analysis in strategic management is to determine every product mix’s current position and determine which SBUs (strategic business units) need more or less investment. Management needs to create the organization’s entire portfolio to analyze the present opportunities and threats to the market and the product.
2. Formulate Growth Strategy
Another aspect that management wants to formulate from the portfolio analysis in strategic management is the growth strategy. According to other products and markets, they develop a different strategy according to their potential threats and opportunities. Portfolio analysis in strategic management helps in laying down the strategy of expansion as well
3. To make decisions Regarding Product Retention
Another reason for corporate portfolio analysis in strategic management is to determine the life of the product:e, to determine which product should be retained longer and which product should be removed from the product line.
These are the three primary and basic reasons for portfolio analysis in strategic management.
Business Portfolio Analysis
Business Portfolio Analysis in strategic management gives importance to the development of strategies equal to the handling of investment portfolios. It is based on the theory of organisational strategy build-up techniques.
Business Portfolio analysis in strategic management shows systematic ways to interpret products and services that form a part of business portfolio analysis. How the financial investments of the firms are treated likewise the appropriate organisational activities should be followed and the inappropriate ones should be disregarded.
Business portfolio analysis forms a part of portfolio analysis in which the company emphasizes that corporate strategies form a significant part of the decision-making for the future accomplishment of the goals.
Process For Portfolio Analysis in Strategic Management
Portfolio analysis in the strategic management process in an organization is as follows:
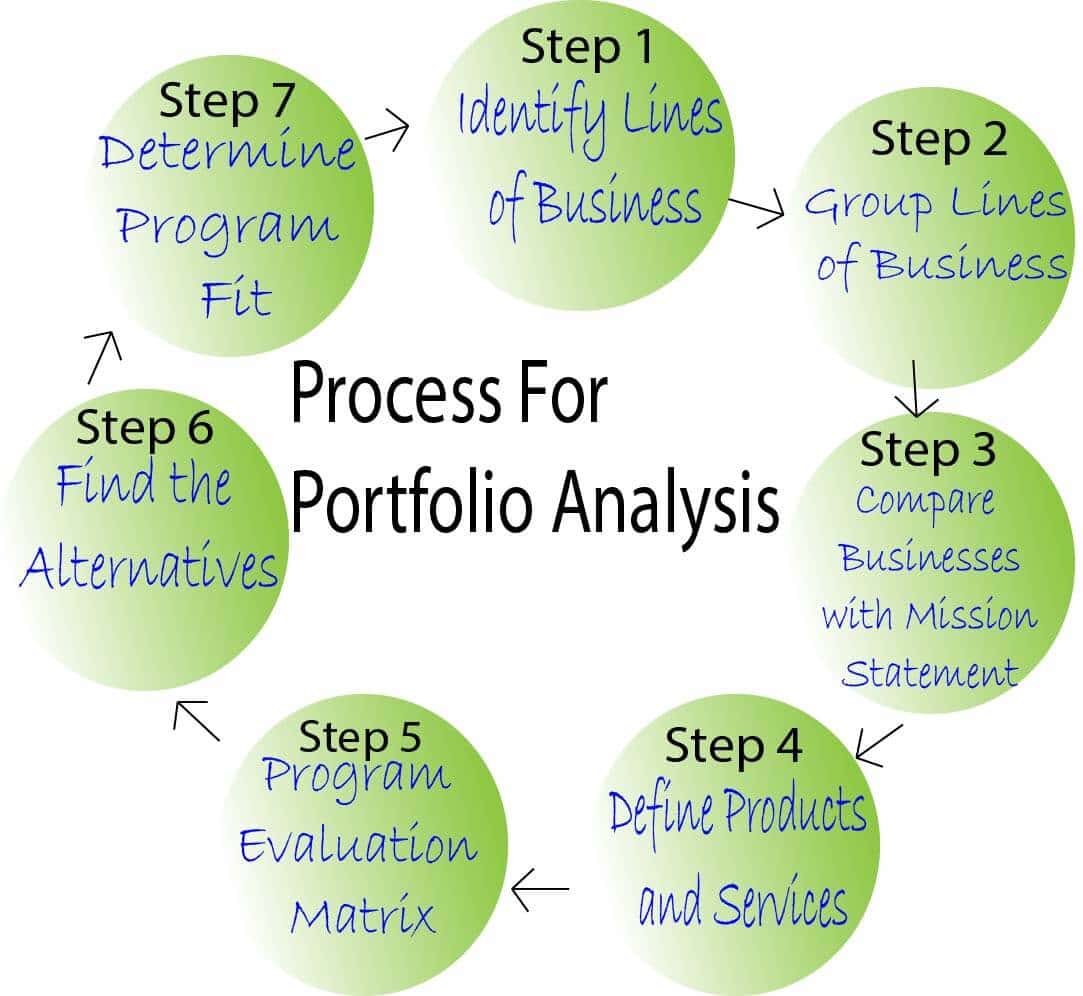
Step 1: Identify Lines of Business
The first step of business portfolio analysis in strategic management is to identify all the current business lines and strategic business units.
Step 2: Group Lines of Business
An organization has three levels of business operation, which are:
- broad membership – directly support the objectives in the strategic plan
- support functions – deliver the core business benefits to members
- money-makers – the source of revenues which support core businesses
Step 3: Compare Core Businesses with Mission
After separating the activities, the next step in portfolio analysis in strategic management is to compare the core starting with the vision and mission and defined goals and objectives. The business should directly support the statements. If the comparison differs, then companies should discontinue allocating the resources in that sector.
Step 4: Define Products in Each Line of Business
The next step of portfolio analysis in strategic management is to categorize each relevant product line;e, subdivide, and define each product relevant product line.
Step 5: Apply the Program Evaluation Matrix
The Program Evaluation Matrix helps in determining the fundamental question of portfolio analysis in strategic management, which are:
- Good fit with our other programs?
- Easy to implement?
- Low alternative coverage in the marketplace?
- Is competitive position strong?
Step 6: Determine the Alternatives
At this stage, the identification of alternatives is made: the competitors. Identification of similar products and their coverage area in the market. The coverage is classified into:
- Low coverage – few comparable programs are offered elsewhere.
- High coverage –many similar programs are offered elsewhere.
Step 7 Determine Program Fit
Ideally, the association will be segregated into two types of programs:
- Well-fitting, accessible programs where the association has a strong position and competes aggressively for a dominant position.
2. Well-fitting, difficult programs with low coverage that the association has the unique, strong capability to provide to essential stakeholders.
This is the repeat process of portfolio analysis in strategic management which takes place in an organization.
Portfolio Management
Portfolio Management explains a process in which individuals’ investments are managed to maximise their earnings given a definite period. Also, it is kept in mind that the invested capital is not exposed to market risk after one limit.
This process of portfolio management depends entirely on the ability to fluctuate with sound decisions. In brief, portfolio management relates to allocating assets and diversifying the resources as per the risk in order to achieve a profitable investment mix.
Initially, portfolio management is a way out of SWOT ( strength, weakness, opportunity, threat) analysis of various investment avenues in comparison to investors’ risk appetite and goals. As a result, this helps the investors to earn and protect them from favourable risks.
Objectives of Portfolio Management
The objective of portfolio management is to select from different investment avenues that best suit the investor depending on various demographic factors like income, period, age and risk.
- Risk optimisation
- Ensuring flexibility of portfolio
- Allocating resources optimally
- Maximising returns on investment
- Capital appreciation
- To improve the overall proficiency of the portfolio
- Protecting earnings against market risks
Types of Portfolio Management
Portfolio management can be broadly classified into 4 types which are as follows :
| 1. Active Portfolio Management 2. Passive Portfolio management 3. Discretionary Portfolio Management 4. Non – Discretionary Portfolio Management |

Active Portfolio Management
This kind of portfolio management is typically aimed at maximising returns. The portfolio manager puts a significant amount of resources into the exchange of securities. Simply the portfolio manager purchases the stocks when undervalued and sells them on the increment of their value.
Passive Portfolio Management
This type of portfolio management aims at fixed-profile designs that are complementary to the current market trends. The portfolio manager here likes to invest in funds with a long-run approach and low but steady returns.
Discretionary Portfolio Management
This portfolio management is typically based on the authority of the portfolio manager and is entrusted to invest on the investor’s behalf. This should be kept in mind that the portfolio manager takes into consideration the risk appetite and goals of the investors and then makes the decision to choose the respective investment strategy whichever is suitable.
Non – Discretionary Portfolio Management
This type is opposite of what has been studied in just above portfolio management. Here the portfolio manager just does the advisory part of investment choices. In this situation is it the choice of the investor whether to take it or reject it. Portfolio management in this case is a suggestion from financial experts to take an opinion from portfolio managers before disregarding them.
Methods for portfolio analysis In Strategic management
Methods of portfolio analysis are different as it depends upon the purpose and product. Here are different methods for portfolio analysis in strategic management:
1. Technological portfolio 2. BCG Growth-Share Matrix 3. Hofer’s Product-Market Evolution Matrix 4. GE Multifactor Portfolio Matrix 5. Market Life Cycle-Competitive Strength Matrix 6. Ansoff’s Product-Market Growth Matrix 7. Arthur D. Little Portfolio Matrix
Project Portfolio Management
Project Portfolio Management is based on the forecasting technique of proposed or current projects. It is a source used by project management organisations and project managers to take into consideration or interpret the potential return occurring out of a project.
Project portfolio management aims to focus on the right potential projects at the right time. They talk more about the delivery and execution of the projects correctly. Project portfolio management involves the analysis of every piece of data of the project which looks forward to investing in newer projects.
Project Portfolio management enables different people to view the bigger picture :
- Executives
- Project managers
- Team managers
- Stakeholders
Product Portfolio Strategy
Product portfolio strategy refers to the list or series of all services and products which are offered by the company. Every business is different and therefore they all have individual ways to schedule their product template and product portfolio strategy. The process of product portfolio strategy involves a variety of decisions.
The Role of Product Portfolio Strategy In Strategic Management
The role of product portfolio strategy is that every product or service whether tangible or intangible is unique and requires a special system. The products can include travel, differ in different situations or include services that need special attention while delivering.
Products can be anything made for the target market and in return provide profits or benefits to the company, organisations, people ideas etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by portfolio analysis?
Portfolio analysis is a process of examining all the aspects related to the organization to improve the organization’s profits.
What is the role of portfolio analysis in strategic management?
The role of product portfolio strategy is that every product or service whether tangible or intangible is unique and requires a special system. The products can include travel, differ in different situations or include services that need special attention while delivering.
What are the methods of portfolio analysis?
Methods of portfolio analysis are different as it depends upon the purpose and product. Here are different methods for portfolio analysis in strategic management:
1. Technological portfolio
2. BCG Growth-Share Matrix
3. Hofer’s Product-Market Evolution Matrix
4. GE Multifactor Portfolio Matrix
5. Market Life Cycle-Competitive Strength Matrix
6. Ansoff’s Product-Market Growth Matrix
7. Arthur D. Little Portfolio Matrix
What is portfolio strategy in strategic management?
Portfolio analysis in strategic management involves analyzing every aspect of the product mix to identify and evaluate all products or service groups offered by the company on the market and to prepare detailed strategies for each part of the product mix to improve the growth rate.