Circular Flow Of Income And Expenditure: It is a model which explains the flow of income and expenditure in the circular flow that illustrates the different sectors in an economy and reveals the different sources of their incomes and the different expenditures which they have to bear.
This model is used in calculating national income, by totalling the income of all the different sectors in the economy.
It is named a circular flow model because money moves in a circular motion in an economy i:e one sector spends money on another sector and receives money from the same sector in a different form.
- To understand the biggest and real-world model which is called four sector model; the explanation starts with smaller and easier models. Classification of the circular flow of income and expenditure different models are;
- Two-sector economy;
- Closed and simple economy
- Includes household and business sectors
- Three-sector economy;
- Open and mixed economy
- Includes household, business, government and capital market
- Four-sector economy;
- Open and mixed economy
- Includes household, business government, capital market and foreign sectors
Explanation of different models in Circular flow of income and expenditure in each sector:
Circular Flow Of Income In Two Sector Economy
The circular flow of income in two sector economy is said as a closed and simple economy. Because the flow of money is taking place between only two sectors; the household sector and the business sector. There is no intervention of government in this form of economy and there are no interactions with the outside economy i:e foreign sector.
The circular flow of income in two sector economy is a closed economy, it has no foreign sector.
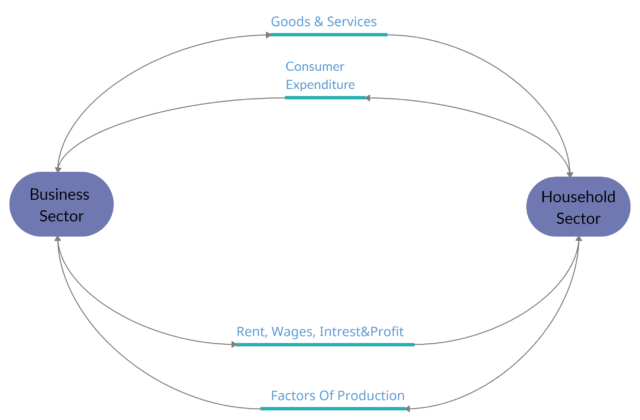
The circular flow of income in two sector economy is illustrated in the above figure.
Household Sector
Household’s different sources of income in the circular flow of income in two sector economy:
- They are the only buyer of goods and services produced by the firms
- They supply the factors of production, i:e land, labour, capital and organization.
- Their entire income is spent on goods and services bought from the business sector.
- Therefore, they do not make any savings and investments.
- They generate income from the factors of production they provided in form of rent, wages, interest and capital.
Business Sector
Business sectors in the two-sector economy:
- The business sector is the producer in an economy, which provides goods and services to households. For this, they receive money from the household sector.
- For producing goods and services the household sector provides the factors of production, land, labour, capital and entrepreneur.
- Pays the household sector in form of rent, wages, interest, the capital.
Equilibrium in the two-sector economy
Equilibrium in the circular flow of income in two sectors when they attain the situation where all two sectors are equal:
i:e. Income (Y) = Consumption (C) = output(O)
Circular flow of income in two sector economy- Assumptions
The circular flow of income and expenditure in two-sector economies is not a real economic model. Assumptions in the circular flow of income in a two-sector economy are:
- There are only two sectors in this model;
- Household
- Business
- No government involvement in economic activities.
- Since there is no foreign sector in this model so there are no import or export activities.
Because of these reasons, circular flow of income in a two-sector economy is a closed economy.
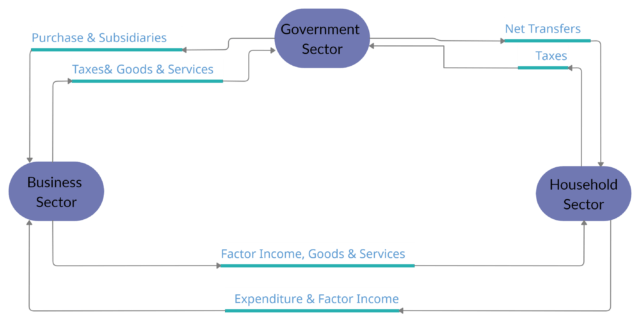
Circular Flow Of Income And Expenditure In Three-Sector Economy
The circular flow of income and expenditure in a three-sector economy includes three sectors-household sectors, business and government sector.
The circular flow of income in three sector economy is not a closed economy but they have no international trade relations.
Circular flow model in three sectors economy explains:
Household Sector
Households in the circular flow of income and expenditure in three sector economy:
- People from the household sector provide a factor of production which are; land, labour, capital and organization.
- For they earn their income in form of rent, wages, interest, the capital.
- The government sector also purchases services from the household sector.
- Household spends their income by purchasing goods and services from the business sector.
- Pay direct and indirect taxes to a government which creates leakages.
- Their entire income is spent on goods and services and taxes.
- Therefore, there is no existence of a financial market in the economy i:e there is no savings and investments in the economy.
Business Sector
Firm’s different sources of income and expenditure in the circular flow of income and expenditure in three sector economy:
- The business sector is the producer in an economy, which provides goods and services to households. For this, they receive money from the household sector.
- For producing goods and services the household sector provides the factors of production, land, labour, capital and entrepreneur.
- Pays the household sector in form of rent, wages, interest, the capital.
- They sell their goods to household and the government and receives payments in return.
- They pay taxes to the government.
- The government sector provides subsidies and other benefits to the firms.
Government Sector
Government sector income and expenditure in the circular flow of income and expenditure in three sector economy:
- The household sector pays direct tax which is also called income tax.
- In return, they provide be various benefits to the household sector like subsidies, welfare etc.
- Firms have to pay taxes for production and profit.
- And, in return firms receives the transfer payments, like- subsidies.
- Also, they buy goods and services from firms/ business sectors.
Financial Market In Circular Flow Of Income In Three Sector Economy
Circular flow of income and expenditure in three sector economy with the financial market:
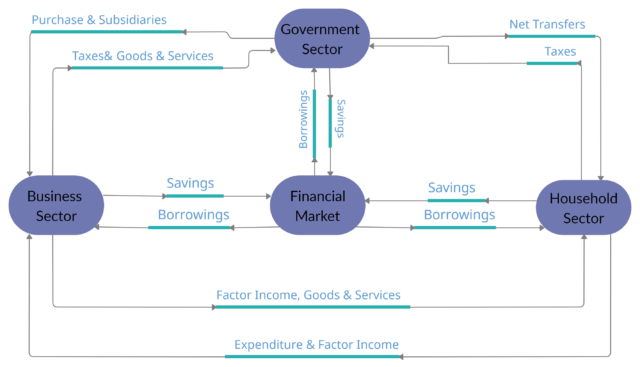
- The capital market receives money from different sectors which is an access portion of their earnings called savings.
- The capital market lends money to firms and the government to increase their resources.
- In the case of financial debt, they provide borrowings to the government sector.
- These borrowings take place as the sale of government bonds and other securities to the public or financial intermediaries.
- An increase in government borrowings results in increases in domestic debt.
- And, when the public sector has a budget in surplus, governments pay off old borrowings, and the rate of payoff is faster than the rate of new borrowing occurs.
Aggregate demand in the circular flow of income in three sector economy is calculated by adding consumption spending (C), investment spending (I) and government spending (G):
Y = C + I + G Where Y is Income, C is Consumption, I am Investment, and Government Spending
Circular Flow of Income In Four Sector Model
The circular flow model in the four-sector economy is a real model which explains the flow of income and expenditure in the real world.
We will study four different sectors in this model; household, firms, government, and foreign. Also, there is the introduction of leakages and injections in this sector.
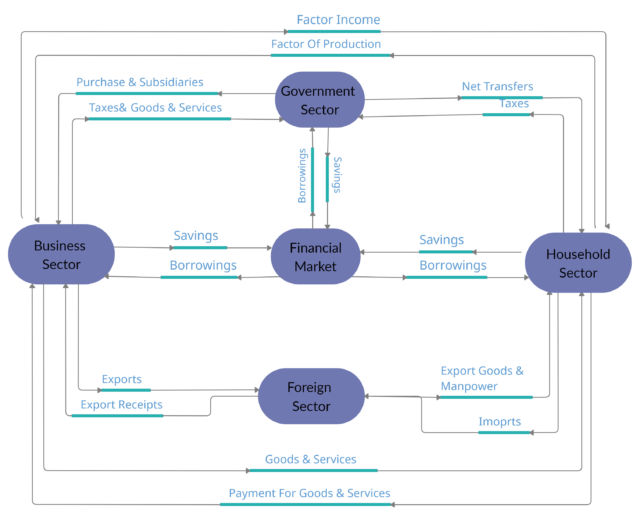
Each sector has a dual function in the circular flow of income and expenditure, as each sector has to make payments to some sectors and receive payments from some sectors.
Circular Flow Of Income In Four Sector Economy
Household Sector
- They are the buyers of goods and services produced by the firms.
- They supply the factors of production, i:e land, labour, capital and organization and receive payments for their supply.
- The household sector pays direct and indirect taxes to the government and firms respectively.
- They also purchases the services from the household and in return, they make transfer payments to the household sector.
- Household Sector exports one of the factors of production i:e, manpower to the foreign sector.
- And there is an existence of imports.
Business Sector
- The business sector is the producer in an economy, which provides goods and services to households. For this, they receive money from the household sector.
- For producing goods and services the household sector provides the factors of production, land, labour, capital and entrepreneur.
- Pays the household sector in form of rent, wages, interest, the capital.
- They pay taxes to the government and also it is one of the factors of leakage from the circular flow.
- The government will purchase goods and provide subsidies and other benefits to firms.
- The business sector borrows funds from the financial market.
- Firms import raw materials from the foreign sector (rest of the world) and business sectors make payment for that.
- Also, firms export their final goods and services to the foreign sector and receive payment for that.
Government Sector
- The household sector pays the income tax and indirect tax imposed on goods and services
- In return, they provide different benefits or transfer payments to them.
- Firms pay taxes to the government, for production and profits.
- They provide subsidies and purchase goods and services from firms.
- The capital market lends money to the government sector in case of a financial deficit
- Also, the government uses the financial market for making their savings and investment.
Foreign Sector
- The business sector makes payments to the foreign sector in return for the goods and services imported.
- They make payments for the imports which they received from the foreign sector.
- Household Sector exports one of the factors of production i:e, manpower to the foreign sector and the foreign sector makes the payment for the same.
- Plus, there are net transfer payments that are made by the foreign sector to households.
Capital Market
- Capital Market receives income from different sectors as they deposit their savings.
- The capital market lends money to the firms or government sector for increasing their resources.
The model can be described using the equation
National Income(Y) = Consumption Expenditure(C)+Investment(I)+Government Expenditure(G)
Including Taxes we get;
National Income (Y) = Consumption Expenditure(C) + Savings(S) + Taxation(T)
Equating the two equations, we get
Consumption expenditure (C) + Investment (I) + Government (G) = Consumption Expenditure (C) + Savings (S) + Taxation (T)
This results to: I + G = S + T
Investments are of two types:
- Domestic Investment (ID)
- Foreign Investment (IF) and get
ID + IF + G = S + T
If IF = Exports (X) – Imports (M)
ID + (X-M) + G= S + T
ID + (X-M) + G= S + (T-G)
This is the equilibrium state of the circular flow of income and expenditure.
Economy Leakages and Injections
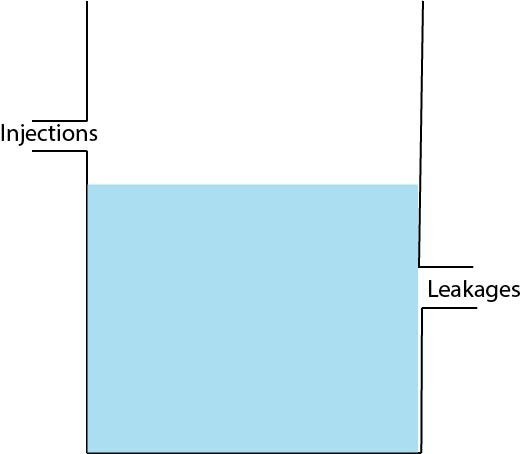
Leakages
- There is a temporary withdrawal of funds from circulation when savings starts in an economy and,
- In the case of imports.
- So, the savings and taxes are called leakages.
Injection
- Exports and foreign investment are the sources of injecting income in the circular flow of income and expenditure.
Total Leakages = Total Injections I+C + G + (X-M) = S+C + Net Taxes S + Net Taxes + Imports = I + G + Exports S = I + (X – M) + (G – NT)
The tank is injected by the investment, government spending and spending by foreigners and its leaks out from savings, taxes and spending on imports. To keep the tank stable i:e to attain equilibrium leakages should be equal to injections.
- In the case of injections > withdrawals or leakages, then the water level in the tank rises.
- If leakages > injections, then the level of water in the tank starts to fall.
- Situations that are required to make injection = leakages are:
- Planned I+G = planned S +T,
- Spending = income and
- Total demand = total supply
- In the case of injections > leakages, then the economy will contract to result in inventory accumulation.
- In the case of leakages > injections, then the economy expands producing more goods and services at higher prices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
what is circular flow of income?
Circular flow of income is a model which explains the flow of income and expenditure in an economy that illustrates the production of goods & services in an economy.
explain the circular flow of income In Two Sector Economy
It is a closed economy in which there are only two sectors households & business sector. The business sector provides repayment of factors on production, goods & services to households. And households provide consumer expenditure & factors of production.
Why Is It Called a Circular Flow Model?
The economy moves in a circle as money flows from one sector to another. One sector spends the money which becomes a source of income for another sector or vice versa.
What is the importance of the circular flow of income and expenditure?
The circular flow of income helps in studying the problems of disequilibrium and restoration of equilibrium. It establishes a link between the producer and the consumer.