What is FMS?
Flexibility manufacturing system or FMS is termed the kind of production method designed to adapt to the changes easily in the quantity and type of the manufactured product. Computerized systems and machines are configured to handle changing levels of production and produce a variety of parts.
The Flexibility manufacturing system thus helps to improve efficiency lowering the company’s manufacturing cost. For example, The system also works as a key component of make-to-order service allowing customers to customize their products according to their requirements.
However, such flexibility may result in higher upfront costs and expensive design. Installing and purchasing the specialized equipment allowing for such customization turns costly compared to traditional systems.

Flexibility manufacturing systems might include a group of numerically controlled machine tools, and interconnected configuration of processing workstations facilitated by computer terminals processing end-to-end development of a product, starting from unloading/loading functions to machining ending assembly to storing to data processing and quality testing.
The system could also be programmed to run a specific batch of one set of products for a particular quantity and automatically switch to another set for another quantity. In the modern scenario, the strategy of flexibility and automation depicts the possibility of manufacturing non-standard areas to develop a competitive advantage.
Objectives of FMS
Formally stated, the objective of flexible manufacturing systems is to gain economies of scale and efficiencies usually connected with mass production.
Moreover to maintain elasticity required for medium and small-lot size production for different parts. Therefore, a generic Flexibility manufacturing system is considered to hold the following components:
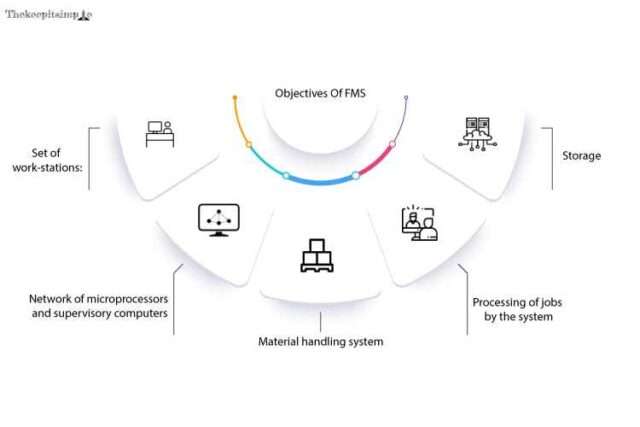
- Set of work-stations: Machine tools that do not need justified change-over or set-up time between successive jobs. These machines typically perform boring, tapping, turning, milling, drilling, reaming, and grooving operations.
- Network of microprocessors and supervisory computers: They perform tasks like keeping track of the status of jobs to know the direction, directing the routes of jobs, providing essential monitoring of the correct performance and finding deviations of the operations. Moreover, passing instructions for working on each operation at every station and ensuring that the rights tools are available.
- Material handling system: Permits the jobs to switch between any pair of machines to follow any job routing as required.
- The processing of jobs by the system: It must be ensured that the employees enter the job on the computer, downloading the part programs to the NC controller or cell control.
- Storage: Centrally at the system level or locally at the workstations.
Benefits of Flexibility manufacturing system
The variable benefits from the utilization and implementation of the flexible manufacturing system are discussed by different researchers.
The increased opportunity of flexible manufacturing technology provides multi-product firms with more variety of choices to assign products to facilities, design production facilities and share capacity among products. An analysis of the literature describes the intangible and tangible benefits that flexibility manufacturing system users highlight as follows:
- Fewer workstations
- Reduced downtime
- Reduced labour
- Work-in-progress inventory or stock reduced
- Increased production flexibility
- Less waste
- Quick changes in dies, stamping delivery and tools
- Better control of quality
- Efficient usage of machinery
- Increased capacity
Moreover, the savings from the above advantages are sizable. For instance, an old example, Ford poured $4,400,000 for overhauling its plant in Chicago (Torrence Avenue), by giving it flexible manufacturing capability.
This allows the company to add new models in lesser time as compared to before. Furthermore, according to a report in Automotive News, five of Ford’s motor company plants yielded $2.5 billion in savings through the flexibility manufacturing system.
Levels of Manufacturing flexibility
Manufacturing flexibility turns a big factor for development in the production system. It further elaborates on the level of competitiveness of different units and the ability to produce goods compatible with the needs of customers.
Now companies face increasingly unpredictable and frequent market test changes because of the persisting global competition, constantly varying product demand and frequent addition of new products. Therefore, it comes important for organisations to follow Flexibility manufacturing system for high-quality products at a lower cost considering the customer needs and market variabilities.
Where variations facilitate what flexibility constitutes, there is a usual differentiation of the core elements. The following are three levels of a flexibility manufacturing system:
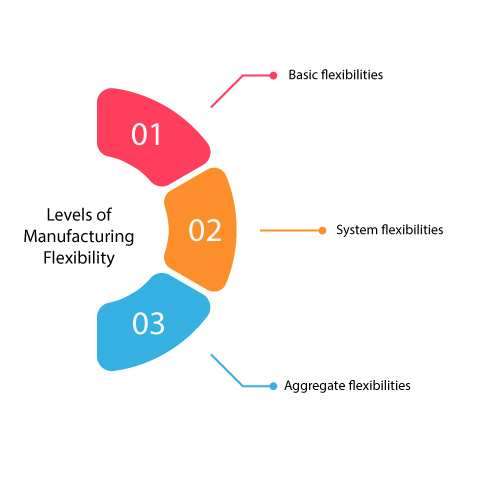
Basic flexibilities
- Material handling flexibility: measures the ease with which different part types can be positioned at various machine tools and transported in a system.
- Machine flexibility: accounts for the smooth path through which machines can process different operations
- Operation flexibility: the ease with which the alternative sequences of the operation can be used for regulating a part type.
System flexibilities
- Expansion flexibility: ability or efficiency to build and expand a system incrementally
- Process flexibility: measures the volume that a set of part types system can produce without requiring any specific setup
- Volume flexibility: counting the system’s capability to operate at different volumes profitably of the existing part types
- Routing flexibility: counts the alternative options or ways that a part can efficiently take through a system in the given process plan
- Product flexibility: undertakes the volume that can be produced of the set of part types in a given system with a minor setup
Aggregate flexibilities
- Production flexibility: undertakes the volume that can be produced of the set of part types without major investment in capital equipment
- Program flexibility: the efficiency of the system to work for longer durations without external intervention
- Market flexibility: the ability of a system to adapt according to the changes in market conditions efficiently
Moreover, there is a concept of Focused Flexibility Manufacturing Systems(FFMSs) that depicts the way to handle the need for customized flexibility and ensure the warranty of optimum trade-off between flexibility and productivity.
This kind of system flexibility affects the architecture of the organisational strategy and explicit design that lead to hybrid systems(automated integrated systems). Here the parts are processed by both dedicated machines and for general purposes.
Process of Flexibility manufacturing system
A flexible manufacturing system components is described as an integrated manufacturing system with handling systems within the control of large computers, transportation and computer-controlled machine tools.
The computer systems are developed or grouped with other devices easily for economical and fast changes in quick responses to the market, and manufacturing process and allowing mass customization of the products. The flexibility manufacturing system can be classified into two types broadly, Routing and machine flexibility. Flexibility manufacturing system furthermore comprises three essential systems:
- The processing stations: Automated CNC machines
- Automated material handling and storage system: Connects with work machines for optimum flow of parts
- Central control computer: Controls the movement of machine flow and materials
Limitations of FMS
Despite the mentioned advantages, Flexible manufacturing system components hold a few limitations which can be studied below:
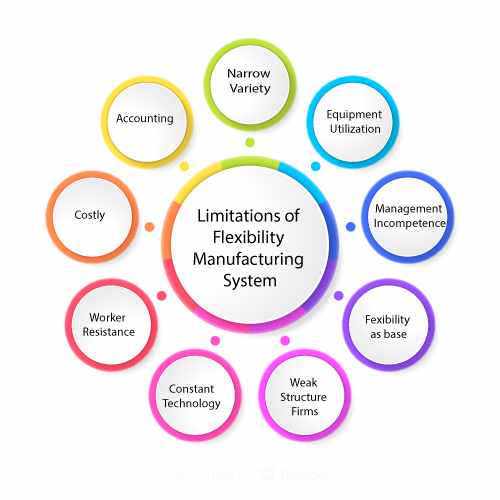
narrow variety
This kind of strategy only handles a relatively narrow variety of ranges. Therefore, it must be used for a family of parts demanding similar processing. Due to the increased cost and complexity of design, a flexible manufacturing system needs longer development and planning span than traditional methods.
equipment utilization
Equipment utilization sometimes for flexibility manufacturing systems is not as high as one expects. For example, the Japanese have a higher utilization rate than U.S. manufacturers that are applying FMS. This is probably the outcome of the U.S. using high volume production for few parts rather than high variety production of various parts at a low cost per unit.
management incompetence
Other drawbacks can be the outcomes of management incompetence, lack of technical literacy, or poor implementation of the system process. If a company misidentifies its goals and mission, without maintaining a production strategy then problems are inevitable.
flexibility as base
The person choosing to compete based on flexibility and the products change rapidly. Then the firm can be a candidate for this scenario, where cost or quality is no main concern.
weak structure firms
Not supportive of firms having weak infrastructure and allocation of resources for implementation. Since new technology requires years to install for being productive and costly.
constant technology
Some firms do not require to change the technological level using flexible manufacturing system components. IBM realised that redesigned printer is easier for manual assembly that could also be achieved at a lower price than automated assembly.
worker resistance
FMS may lead to worker resistance. They tend to believe automation is the purpose the replace them with technology that does not take rest, and neither requires training. This perception may lead to firm stress for the flexibility manufacturing system installation.
costly
The maintenance, personal training and energy costs are expected to be higher. Shortened product lifecycles and rapidly changing technology may cause the capital equipment to become obsolete faster.
accounting
FMS can turn out to be a difficult task when accounting tends to design for mass production. For a mature product along with stable technology and known characteristics.
Therefore, it becomes challenging to give away an apt indication of whether flexibility manufacturing system is justified or not. The question also arises about the ways to quantify the advantages of flexibility.
Although the advances have been shown in low to mid-volume and high-mix production applications. As a result, firms continue to use flexible manufacturing system components to compete on technology advances and flexibility basis.
Conclusion
Flexibility manufacturing system thus explains the response of the organisational system to internal and external changes affecting the value delivery in a cost-effective and timely manner. It further highlights the possible levels of flexibilities which are basic, system nd aggregate flexibilities. The concept of manufacturing going beyond a flexibility system is termed agile manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is flexibility in a manufacturing system?
A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a production method that is designed to easily adapt to changes in the type and quantity of the product being manufactured. Machines and computerized systems can be configured to manufacture a variety of parts and handle changing levels of production.
What is flexible manufacturing system example?
Examples of FMS include: Assembly lines are used in industries like car manufacturing, where one product moves through a series of processes, each performed by one machine. Robots are programmable machines that can perform specific tasks in a manufacturing setting.
What are the 3 levels of manufacturing flexibility?
- Basic flexibilities
- System flexibilities
- Aggregate flexibilities
What are the features of flexible manufacturing system?
The key features of a Flexible Manufacturing System:
- Random bypass capability
- Automation
- Competent redundancy
- Multiple paths